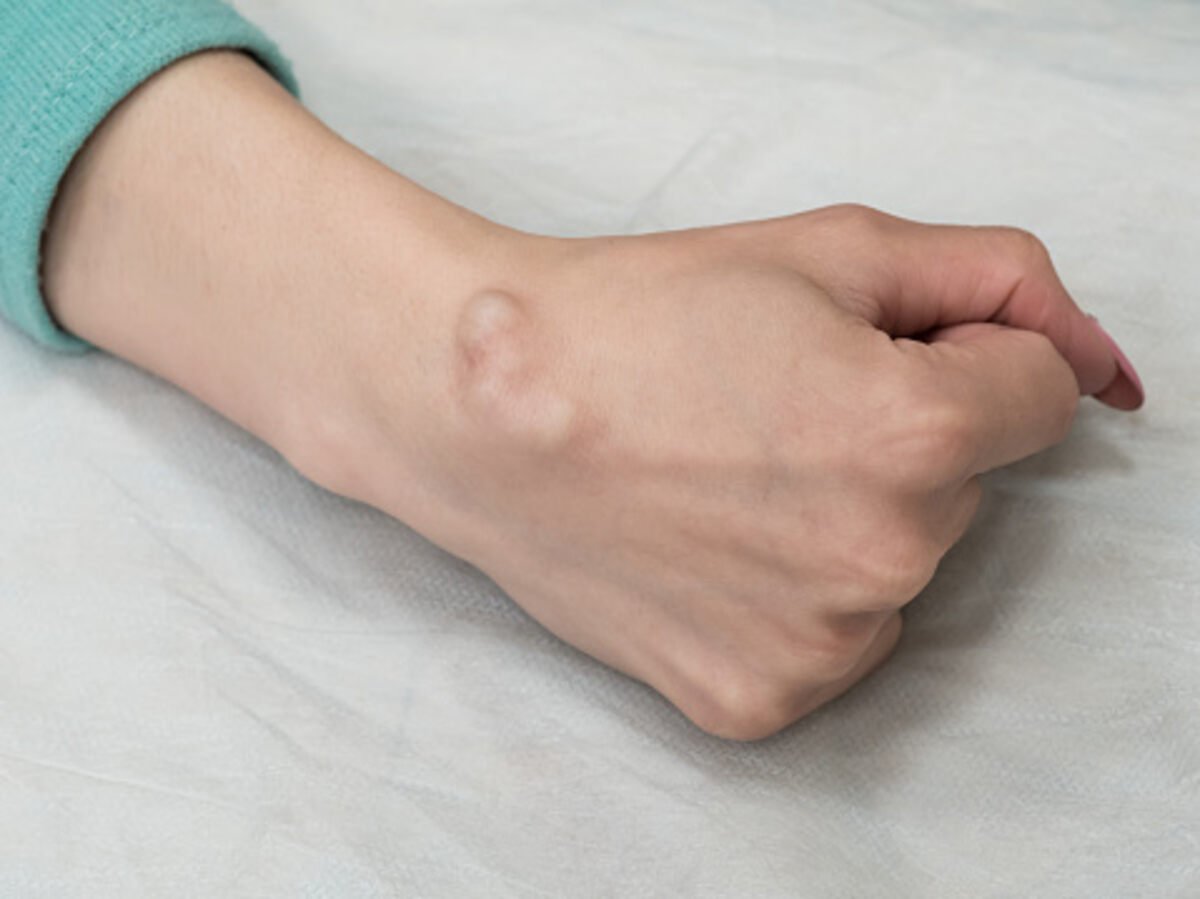
What is a Cyst?
A cyst is a pocket that develops under the skin filled with fluid. Several factors can cause cysts. They can trap sweat glands, blood, fat, teeth, and other structures. Fluids that build up can also become trapped in the folds, resulting in small lumps or swellings. Treatments include surgery.
Symptoms
Cysts are small swellings on the skin that can grow to a large size. They can occur on the skin anywhere on the body and are most commonly painless. However, some cysts can grow deep inside the body and cause other symptoms. If you are worried about the appearance of a cyst, you should visit a dermatologist, who can help you to know the symptoms and treatment options for your particular case.
Cysts are closed sac-like structures filled with gas, liquid, and semisolid material. They can range in size from microscopic to large and can even displace internal organs. Most cysts are benign, but some are infectious. Therefore, the best way to diagnose a cyst is to perform a medical examination and determine whether a cyst is present.
Cysts are typically painless, although there are some cases where you may notice a painful cyst or bleeding. It is essential to consult a doctor if the pain from a cyst persists and if you think you have a cyst because you may need regular checkups to monitor its progress. A doctor may prescribe you painkillers for the pain.
Causes
Cysts are sac-like structures, usually filled with liquid, semisolid, or gas. They can develop in almost any tissue in the body. They range in size from microscopic to massive and sometimes displace internal organs. While most cysts are benign, some can be cancerous. Therefore, identifying the underlying cause is essential to determine the best treatment option.
Some people may need to go to the hospital to treat a cyst. The treatment option depends on the cyst’s size, location, and extent. In some cases, surgery is necessary to remove the cyst. Cysts can enlarge rapidly within a short period. If the cyst ruptures, it can cause severe complications. For example, a ruptured cyst in the abdomen or pelvic area can lead to severe contamination of the peritoneum or pelvic cavity.
Cysts can be painful or non-painful. There are two main types of cysts, epidermoid and sebaceous. Epidermoid cysts are made of keratin and fat and may develop due to an injury. Although they look similar, epidermoid cysts are less painful than sebaceous cysts. On the other hand, Sebaceous cysts are formed from the oil-producing sebaceous glands. Acne is a risk factor for developing sebaceous cysts.
Treatments
There are several different cyst treatments available, and a healthcare professional can recommend a treatment based on the type and location of your cyst. Most cysts have no symptoms, but they can be painful and irritating. In addition, they may be stiff, inflamed, and sometimes even infected. Cysts may be caused by several factors, including a blockage of a duct or a defect in the cells. Some cysts can also form due to chronic inflammation and fluid buildup in the body.
There are hundreds of different types of cysts. Some of them are skin cysts, which can appear anywhere on the body. Some common areas for skin cysts include the face, scalp, and genitals. They are also standard on the back, shoulders, and underarm pits. A dermatologist can quickly diagnose whether a cyst is present on the skin by visually inspecting the lump. There are also a variety of treatments available, including home remedies and medical procedures.
Some cysts are large and may need to be surgically removed. This is often recommended when a cyst is so large that it interferes with an organ’s function or if the cyst is infected. No treatment is required if the cyst is small and produces no symptoms. Cysts in the brain, however, may be a sign of cancer and require surgery.
Prevention
Prevention of cysts is vital for healthy living and can be achieved by lifestyle changes. For example, eliminating alcohol and caffeine from your diet, increasing your vitamin A and carotenoid intake, and consuming more whole grains are great ways to prevent and manage cysts. Other healthy lifestyle choices include increasing omega-3 essential fatty acids and iodine.
Generally, cysts develop due to localized infection or damage to a gland. They may also form due to a defective or blocked secreting duct. However, some cysts may not be visible to the affected person. These cysts can form in tendons, breasts, and other tissues. Depending on size and location, they can cause pain and other symptoms.
The best way to prevent cysts is to understand their causes and how to prevent them from returning. Most cysts are harmless, but you may need medical attention if they start reoccurring. Treatment options for cysts can include medications, physical therapy, and a surgical drain.